오늘은 알고리즘을 기초부터 시작해보기 위해GeeksForGeeks라는 사이트에서 자료 구조 및, 정렬 알고리즘 등을 찾아보았다. 그 중, Array 관련 문제중, rotate Array를 사이트 문제에서 찾아 구현해보았다.
practice.geeksforgeeks.org/problems/rotate-array-by-n-elements/0#
Rotate Array | Practice | GeeksforGeeks
practice.geeksforgeeks.org
문제
Given an unsorted array arr[] of size N, rotate it by D elements (clockwise).
Input:
T : testcase의 개수
N : array의 Size
D : rotation의 Size
Output:
For each testcase, in a new line, output the rotated array.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 200
1 <= N <= 107
1 <= D <= N
0 <= arr[i] <= 105
Example:
Input:
2
5 2
1 2 3 4 5
10 3
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Output:
3 4 5 1 2
8 10 12 14 16 18 20 2 4 6
Explanation :
Testcase 1: 1 2 3 4 5 when rotated by 2 elements, it becomes 3 4 5 1 2.
코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class RotateArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
int testCase = Integer.parseInt(bufferedReader.readLine());
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < testCase; i++) {
List<Integer> input = Arrays.asList(bufferedReader.readLine().split(" ")).stream()
.map((s) -> Integer.parseInt(s)).collect(Collectors.toList());
int n = input.get(0);
int d = input.get(1);
Integer[] srcArr = new Integer[n];
Integer[] tmpArr = new Integer[d];
Arrays.asList(bufferedReader.readLine().split(" ")).stream().map((s) -> Integer.parseInt(s))
.collect(Collectors.toList()).toArray(srcArr);
for(int j=0; j<d; j++) {
tmpArr[j] = srcArr[j];
if(j+d<n)
srcArr[j] = srcArr[j+d];
}
int index = d;
while (index <= n - 1) {
if (index + d >= n)
break;
srcArr[index] = srcArr[index + d];
index++;
}
for (int j = 0; j < d; j++) {
srcArr[n - d + j] = tmpArr[j];
}
for (int src : srcArr) {
stringBuilder.append(src + " ");
}
if (i != testCase - 1)
stringBuilder.append("\n");
}
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
예제로 나온 코드
// Java program to rotate an array by
// d elements
class RotateArray {
/*Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d*/
void leftRotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++)
leftRotatebyOne(arr, n);
}
void leftRotatebyOne(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, temp;
temp = arr[0];
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
arr[i] = temp;
}
/* utility function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
RotateArray rotate = new RotateArray();
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
rotate.leftRotate(arr, 2, 7);
rotate.printArray(arr, 7);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
결과
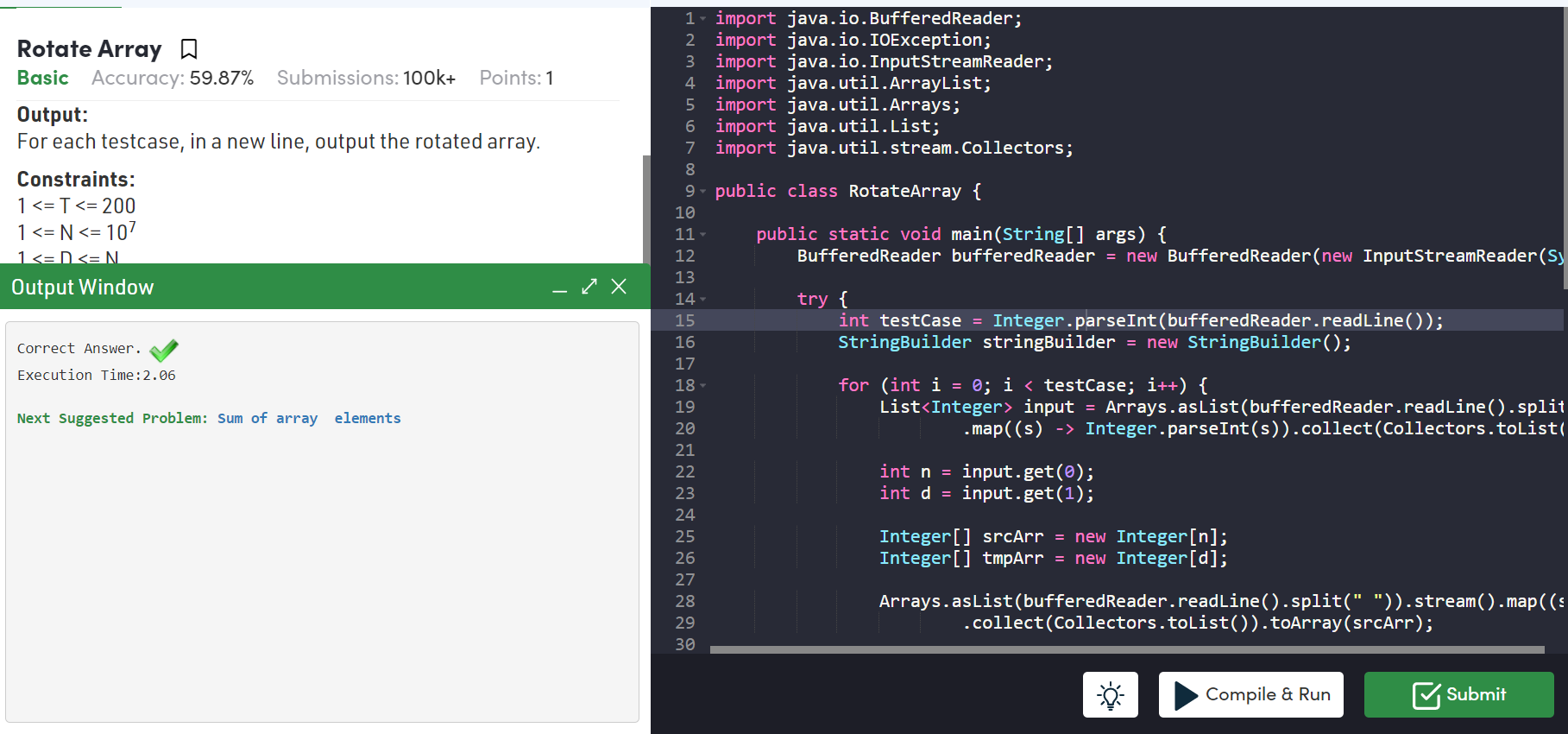
😒 이번에는 input data를 입력받을 때 ,저번에 배워둔 collection stream을 사용해보고 싶어 적용해 보았다.
🤔 정작 풀고나니 그렇게 어렵다고 생가하지 않았지만..
🤢 처음 문제를 풀 때 이상한 곳에 포인트를 두고, 문제 해석 자체를 정확하게 해내지 못해서 예상보다 시간이 걸렸다. 그리고 답안지 코드와 내 코드를 비교해보니 아직 많이 부족한 점을 느꼇다..
😜 정신좀 똑바로 차리고 살아야 겠다.
* 위에서 제시한 코드 이외에도 여러 방법이 나와있고, 각각 친절하게 원리와 시간복잡도 및 공간복잡도가 명시되어있으니 필요하면 직접 사이트에서 봐보는것을 추천한다.
www.geeksforgeeks.org/array-rotation/
Program for array rotation - GeeksforGeeks
A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
www.geeksforgeeks.org